Group A
Multiple Choice Questions (11×1 = 11)
1. What is the equivalent weight of H3PO3 in
the reaction; 2NaOH + H3PO3 → Na2HPO3 +
2H2O
A) 2M
B) M/1
C) M/2
D) M/3
2. The solubility product of chalk is 9.3 × 10-8.
What is its solubility in gram per liter?
A) 3.04 × 10-1
B) 3.04 × 10-2
C) 3.04 × 10-3
D) 3.04 × 10-4
3. What is the concentration of N2O5 in the
following first-order reaction in which the rate is 2.4 × 10-5 mol/L
and rate constant is 3.0 × 10-5S-1?
2N2O5 → 4NO2 + O2
A) 0.04
B) 0.8
C) 1.2
D) 1.4
4. What happens when the lead storage battery is discharged?
A) SO2 is evolved
B) PbSO4 is consumed
C) Lead is formed
D) H2SO4 is consumed
5. What is the general electronic configuration of
transition metal?
A) (n-1)s2p6d1-10ns0-2
B) (n-1)s2p6ns2np1
C) (n-1)s2p6d5ns1
D) (n-1)s2p6ns1
6. Which of the following ore is concentrated by
forth-flotation process?
A) Hematite
B) Siderite
C) Galena
D) Malachite
7. Which of the following products is obtained when
nitrobenzene is electrolytically reduced?
A) P-aminophenol
B) azobenzene
C) azoxybenzene
D) hydrazobenzene
8. Which of the following compounds is a pi-bonded
organo-metallic compound that has ethene as one of its components and is the
first synthesized organometallic compound?
A) Zeise‟s salt
B) Ferrocene
C) Dibenzene chromium
D) Tetraethyl tin
9. What effect does calcium sulphate have on cement?
A) Retards setting action
B) Acts as flux
C) Imparts color
D) Reduces strength
10. Removal of which of the following leads to higher
fiber-fiber bonding strength in the paper?
A) Softwood
B) Hardwood
C) Lignin
D) Pulp
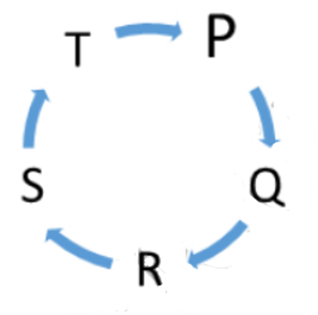
11. In the figure given below which one is correct?
A) Alpha rays deviate towards A, beta rays deviate towards C
and gamma rays direct towards B.
B) Alpha rays direct towards B, beta rays deviate towards C and gamma rays
towards A.
C) Alpha rays deviate towards C, beta rays direct towards B and gamma rays
towards A.
D Alpha rays deviate towards C, beta rays deviate towards A and gamma rays
direct towards B.
Group B
Short Answer Questions (8×5 = 40)
1. Standard solution of Na2CO3 is
used to determine the strength of H2SO4 during Titration.
A) How is the completion of the reaction in this titration
detected? Is the solution prepared from Na2CO3 primary
standard? Why? [1+1]
B) 2.16 g of pure Na2CO3 is added to 400 ml
deci-normal solution of H2SO4. How many grams of H2SO4 is
further required to neutralize the resultant solution completely? [3]
OR
A) Derive the relation k =log(2.303/t) log(a/a-x) . Show
that for the first-order reaction the time required for half the change
(half-life period) is independent of the initial concentration. (2+1)
B) A first-order reaction is 50% completed in 1.26×10145. How much
time would it take for 90% completion? (2)
2. Study the following data for the thermodynamic process H2O
(l) → H2O (s) at different temperatures and at 1 atmospheric pressure.
|
Condition |
Temperature |
Entropy Change in J/Kmol-1 |
|
|
|
|
Entropy of System |
Entropy of surrounding |
|
1 |
-1 0C |
-25.68 |
+25.72 |
|
2 |
0 0C |
-26.55 |
+26.88 |
|
3 |
+1 0C |
-27.62 |
+27.42 |
- Calculate
the total entropy of the universe at given condition 3. (1)
- Can we
predict the spontaneity of the given reaction at 0°C? (1)
- Calculate
the equilibrium constant for the fusion of ice at 1°C. What is the effect
of temperature for the entropy change of reaction? (2+1)
3. The figure shows the octahedral distortion of d-block orbital in the
presence of a ligand.
- Why
does octahedral distortion occur in the presence of ligand? Explain on the
basis of CFT. (2)
- On the
basis of the given distortion, how can you explain [Cu(H2O)6]++ is
blue colored complex. (1)
- Out of
Fe++ and Fe+++ which one is more stable?
Explain on the basis of distortion seen in the above figure. (1)
- Why do
such elements which give such splitting show good catalytic properties?
(1)
4. X is an ore of a metal M. X on calcination gives black precipitate (W) of
metal oxide which belongs to group II of basic radical in qualitative analysis.
X on roasting gives the metal (M) and gas as major byproducts. The gas when
passed through an acidified K2Cr2O7 solution
turns green.
- Identify
the metal X. (1)
- Write
the reaction involved during calcination of X. (1)
- Write
the action of the gas on acidified K2Cr2O7.
(1)
- Convert
metal X into it’s vitriol. (2)
5. The given table shows the compounds and their molecular formula. How can you
convert P to Q, where Q is a compound in which two methyl groups are
substituted at adjacent carbons? How is P obtained from T, where T is secondary
alcohol? Write the reactions involved in the conversion of P into R and S?
[5×1=5]
|
Compounds |
Molecular Formula |
|
P |
C3H7Br |
|
Q |
C6H14 |
|
R |
CH2O |
|
S |
C2H4O |
|
T |
C3H8O |
OR
An aromatic compound [A] in which one chlorine atom is
substituted at a benzene ring. When the compound [A] is heated with 2, 2,
2-trichloro ethanal in presence of conc. H2SO4 gives
an insecticide [B]. The compound [A] when treated with an acid
chloride-containing two carbon atoms in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 gives
[C].
- Identify
B and C. (1 +1)
- Reaction
of aq. NaOH on the compound [A] is more difficult than with chloroethane,
justify with a suitable explanation.(2)
- How
would you obtain compound A from benzene diazonium chloride? (1)
6. A list of compounds are given as follows:
p-hydroxyazobenzene,
C6H5N2Cl, C6H5NH2,
C6H5NO2, C6H6
From the above list of compounds, prepare a sequence of
reaction chains with suitable conditions and reactions. (1+1+1+1+1)
7. Write down the isomeric alcohols of C3H8O and their IUPAC
name. How would you apply Victor Meyer’s test to distinguish these isomers?
(2+3)
8. A) Define condensation polymerization. Write the
molecular structures of monomers of Bakelite. (1+2)
B) Differentiate between OPC and PPC cement.
Group C
Long Answer Questions (3 × 8 = 24)
9. (A) What amount of Zn(OH)2 will be precipitated out at 25°C
if 100 ml of 0.22gm NaOH is added to 1 liter of a saturated solution of Zn(OH)2?
Precipitate is obtained in this reaction, why? [Solubility product of Zn(OH)2 at
25°C is 1.8 x 10-14]
(B) Potassium hydroxide having pH 8 is diluted 1000 times. Calculate the pH of
the diluted base. (3)
OR
(A) Calculate heat of formation of ethyl alcohol from the
given data. (4)
|
Heat of combustion of ethyl alcohol |
-330 kcal |
|
Heat of formation of Carbondioxide |
-94 kcal |
|
Heat of formation of water |
-68.5 kcal |
(B) The standard electrode potential for the following
electrode reaction at the standard state is given.
Cu(s) → Cu++ (aq) + 2e–………E0 Cu++/Cu=
+0.34V
Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s) …………E0 Ag+/Ag=+0.80V
- Write
the cell notation indicating anode and cathode. (1)
- With 1M
solution of ion at 25°C and 1atm. pressure, what will be the cell
potential? (1)
- Calculate
the free energy change in the reaction. (1)
- Can we
store AgNO3 solution in a copper vessel? (1)
10. (A) A primary alcohol with molecular wt. 46 is boiled with sodium hydroxide
and iodine. When the same alcohol is heated with ethanoic acid in presence of
conc. H2SO4, one of the derivatives of the carboxylic
acid is obtained. Write the reactions involved in both conditions. What would
be the product obtained when the same alcohol is heated with conc.H2SO4?
How would you distinguish the above alcohol from methanol? [1+1+1+1+1=5]
ent. (2)
(B) An aromatic compound known as oil of mirabane is
prepared from benzene.
a. What product would you obtain when the compound is
electrolyzed in the acidic medium? (1)
b. Give the complete reaction for the conversion of the compound into the yellow
dye. (2)
11. (A) An organic compound is used in the given figure to
preserve museum specimens and also to prepare urinary antiseptics.
- Write
the reaction when the compound is heated with concentrated sodium
hydroxide. (1)
- Draw
the structure of urinary antiseptic (1)
- Write
the chemical reaction that would occur when the given preservative is
treated with phenol in acidic medium. (2)
- How
would you obtain the preservative from methanol? (1)
(B) A carbonyl compound with molecular formula C3H6O (it
does not give silver mirror test) has treated with a compound Y which gives Z.
Z on hydrolysis in acidic medium gives 2-hydroxy-2-methyl propanoic acid.
Identify the carbonyl compound, Y and Z with proper reactions. [1+1+1]
OR
(A) Starting from compound P, how do the reactions proceed ahead to obtain T which gives benzene where R is aniline? Complete the reaction sequence with suitable conditions. [5×1=5]
(B) Arrange the given compounds according to their ascending
order of acidic strength and justify your order.
CH3CH2COOH, C6H5COOH, ClCH2CH2COOH
[1+1+1]
Disclaimer: Copying our content and publishing on own website is strictly prohibited.