Aniline, Benzene diazonium Chloride , Benzonitrile, Benzamide, Benzoic Acid.
Solution:

b) Write the name of aldehyde which gives tollens test and shows aldol condensation.
Solution:

c) How is 2- Hydroxy propanoic acid obtained from Ethanal.
Solution:

2. a) Write the structure A, B and C in the following:
Ans:
Compound A is Aniline
Compound B is benzene diazonium chloride salt.
Compound C is iodobenzene.
b) What happened when C is heated with sodium metal in presence of dry
ether?
Ans: When Iodobenzene is heated with sodium metal in presence of
dry ether it gives biphenyl as shown in the reaction given below:
c) What product would you get when compound A and compound B are
heated.
Ans: When compound A and compound B are heated, we will get P amino azobenzene.
3. a) An organic compound a which characteristic order, on treatment with
NaOH Forms two compounds B & C which on oxidation with CrO3
gives back compound A. Compound C is the sodium salt of acid. Compound C
when heated with soda lime yields an aromatic hydrocarbon D. Deduce the
structure of A, B, C and D. Write down the chemical equation for all the
reaction taking place.
Solution:
b) Why NH2 group of aniline is protected before nitration?
Solution:
To prevent unwanted side reactions and to ensure selective nitration at the
ortho and/or para positions. Aniline contains a reactive amino group (-NH2)
that can react with nitric acid during the nitration reaction, leading to
the formation of undesirable by-products. For example, the amino group can
be nitrated, leading to the formation of di- and tri-nitroanilines instead
of mono-nitroanilines. These by-products are difficult to separate from the
desired product and can reduce the overall yield of the reaction.
c) Write a product which is obtained by the reduction of acetic
anhydride.
Solution:
CH3CO−O−COCH3 (acetic
anhydride)+LiAlH4→C2H5−OH (Ethanol)
4. Give Reason:
a) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta
position.
Ans: Benzoic acid has a deactivating carboxylic group that decreases
electron density at ortho and para positions. This makes the meta position
more favorable for electrophilic substitution as it has higher electron
density. Therefore, electrophiles attack at the meta position rather than
ortho and para positions.
b) Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reaction of carbonyl
group.
Ans: The carbonyl carbon in carboxylic acids exhibits reduced
electrophilicity due to resonance, which is why carboxylic acids do not show
characteristic reactions of the carbonyl group.
(c) Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones,
and alcohols of comparable molecular masses.
Ans: Carboxylic acids have strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding, leading to extensive molecular association. As a result, they have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones, and alcohols of similar molecular weight.
5. a)
An organic compound a with molecular formula C8H8O
and gives yellow precipitate with 2,4-DNP on heating with iodine in the
presence of sodium hydroxide. It neither reduces tollens’ or Fehling’s
reagent nor does it decolorize bromine water or Bayer’s reagent. On
drastic condition with chromic acid, it gives a carboxylic acid B having
molecular formula C7H6O2. Identify
compound A&B and explain the reaction involved.
b) An organic compound Z is known as an oil of mirbane which is prepared
by nitration of benzene.
i. What product would you expect when Z is reduced with LiAlH4.
ii. Convert Z into P hydroxy azobenzene.
Solution:
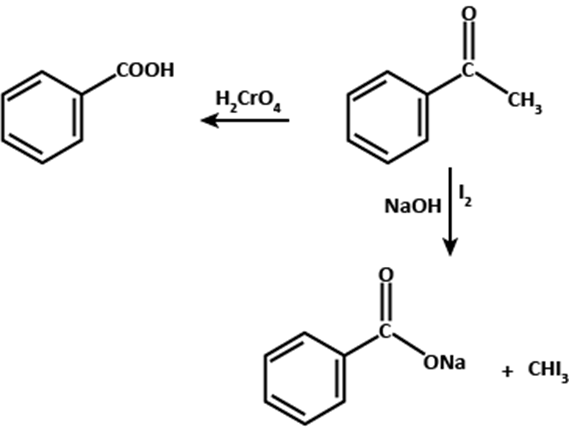
A)
Identifying Compound, A:
Compound (A) is characterized by the formation of a 2,4-DNP derivative,
which suggests that it may be either an aldehyde or a ketone. However, since
it does not reduce Tollens' or Fehling's reagent, it can be concluded that
Compound (A) is a ketone. Additionally, it gives a positive iodoform test,
indicating that it is a methyl ketone.
Although Compound (A) has a molecular formula of C₈H₈O, which suggests a
high degree of unsaturation, it does not decolorize bromine water or
Baeyer's reagent. This indicates that the unsaturation is due to the
presence of an aromatic ring in the molecule.
Further evidence for the identity of Compound (A) comes from its reaction
with NaOH and I₂, which gives a positive iodoform test. This confirms that
Compound (A) is a methyl ketone with an aromatic ring.
Taking all these observations into account, it can be concluded that
Compound (A) is phenyl methyl ketone, also known as acetophenone, with the
molecular formula C₈H₈O.
Identifying Compound B:
Compound (B) with the molecular formula C₇H₆O₂ is oxidized to form a
carboxylic acid.
Based on this information, it can be concluded that Compound (B) is benzoic
acid.
The chemical equation for the oxidation of Compound (B) to form benzoic acid
is:
C₇H₆O₂ (Compound B) + 3[O] → C₇H₆O₂ (Benzoic acid) + H₂O
Therefore, the compound (B) is benzoic acid, which can be represented by its
molecular formula C₇H₆O₂.
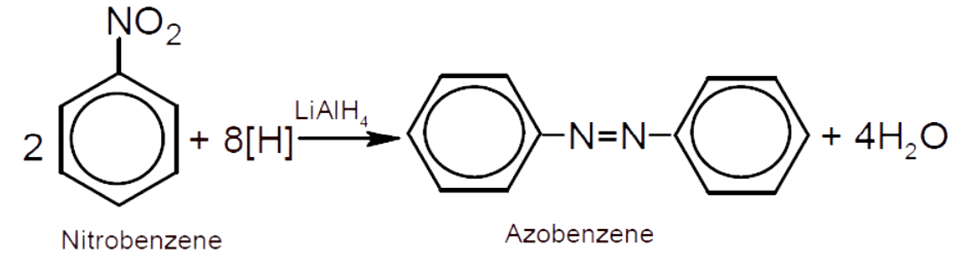
b) Since Z is oil of mirbane i.e., nitrobenzene which can be easily
prepared by nitration of benzene.
i) Nitrobenzene on reduction with lithium aluminum hydride
(LiAIH4) gives azobenzene.
ii) Conversion of Oil of Mirbane (Comp. Z) i.e., Nitro benzene into P
Hydroxy azobenzene involves the following reaction
6. a) Arrange the following compound in increasing order of basic
strength in their aqueous solution
NH3, CH3NH2,
(CH3)2NH,
(CH3)3N.
b) Give you a chemical test to distinguish between ethylamine and
aniline.
c) How can methyl bromide be preferentially converted to methyl
isocyanide?
d) Complete the following reaction equations:
i. C6H5N2Cl + H3PO2
+ H2O →
ii. C6H5NH2 + Br2 →
Solution:
a) CH3NH2, > (CH3)2NH
> (CH3)3N
b) Solution will be available soon.
c) CH3Br (Methyl Brommide)+AgCN→CH3NC (Methyl
Isocyanide)+AgBr
d) (i)
d(ii)