Sub. code. 1021
NEB-XII 2079(2023)
Model Question
Physics
Candidates are required to give answers in their own
words as far as practicable. Figures in the margin indicate full marks.
Time: 3hrs
Full Marks: 75
Attempt all the questions.
Group – 'A'
Rewrite the correct options of each question in your
answer sheet. (11x1=11)
1. The product of moment of inertia and angular velocity
gives
(A) Force
(B) Torque
(C) Linear Momentum
(D) Angular Momentum
2. The bob of a simple pendulum has a mass of 0.40 kg. The
pendulum oscillates with a period of 2.0 s and an amplitude of 0.15m. At an
extreme point in its cycle, it has a potential energy of 0.044J. What is the
kinetic energy of the pendulum bob at its mean point?
(A) 0.022 J
(B) 0.044 J
(C) 0.011 J
(D) 0.033 J
3. What causes earthquakes?
(A) The flow of magma
(B) The expansion of the earth’s crust
(C) The rubbing together of earth’s plates
(D) Tsunami
4. What percentage of original radioactive atoms is left
after 4 half-lives?
(A) 1%
(B) 6%
(C) 10%
(D) 20%
5. Two wave pulses travel toward each other as shown in the diagram below.
Which of the following diagrams represents the superposition of the pulses when they meet?
6. Which one of the following properties of sound is
affected by the change in air temperature?
(A) amplitude
(B) frequency
(C) wavelength
(D) intensity
7. Internal energy of an ideal gas depends on
(A) volume only
(B) pressure only
(C) temperature only
(D) both pressure and volume
8. In which of the following processes of the gas, work done
is the maximum?
(A) Isothermal
(B) Isobaric
(C) adiabatic
(D) Isochoric
9. The neutral temperature of a thermocouple is equal to
500°C when the temperature of cold junction is 0°C. Percentage change in the
temperature of inversion when temperature of cold junction is equal to 20°C is
(A) 2%
(B) 3%
(C) 4%
(D) 5%
10. In which of the following circuits the maximum power
dissipation is observed?
(A) a circuit having inductor and resistor in series
(B) pure resistive circuit
(C) pure inductive circuit
(D) pure capacitive circuit
11. Why laminated cores are placed in transformers?
(A) to reduce hysteresis loss
(B) to reduce eddy current
(C) to reduce the magnetic effect
(D) to increase coercivity
Group ‘B’
12. (i) Define simple harmonic motion.
(ii) Derive an expression for the time period of oscillation
for a mass m attached to a vertical spring of force constant k.
(iii) What will be the time period of this system if it is
taken inside the satellite?
13. (a) State Bernoulli’s principle.
(b) Figure below shows a liquid of density 1200kgm-3
flowing steadily in a tube of varying cross-sections. The cross-section at
point A is 1.0 cm2 and that at B is 20 mm2, points A and
B are in the same horizontal plane. The speed of the liquid at A is 10 cm/s.
Calculate
(i) the speed at B.
(ii) the difference in pressure at A and B.
14. (a) Draw a PV diagram of a petrol engine and explain its
working based on its PV diagram.
(b) Compare the efficiency of petrol engine with that of
diesel engine based on their compression ratios.
15. (a) When the wire of a sonometer is 75 cm long, it is in
resonance with a tuning fork. On shortening the wire by 0.5 cm it makes 3 beats
with the same fork. The beat is the difference in frequencies. Calculate the
frequency of the tuning fork.
(b) The diagram below shows an experiment to measure the speed of a sound in a string. The frequency of the vibrator is adjusted until the standing wave shown in the diagram is formed.
The frequency of the vibrator is 120Hz. Calculate the speed
at which a progressive wave would travel along the string.
16. (a) State Lenz law in electromagnetism. Justify this law
is in favor of the principle of conservation of energy.
(b) A magnet is quickly moved in the direction indicated by an arrow between two coils C1 and C2 as shown in the figure. What will be the direction of induced current in each coil as indicated by the movement of magnet? Explain.
17. (a) State the principle of the Potentiometer. A
potentiometer is also called a voltmeter of infinite resistance, why?
(b) In the meter bridge experiment, the balance point was
observed at J with l=20cm
(i) The values of R and X were doubled and then
interchanged. What would be the new position of balance point?
OR
(a) State the two Kirchhoff’s laws for electrical circuits.
(b) In Meter Bridge shown below, the null point is found at
a distance of 60.0 cm from A. If now a resistance of 5 ohm is connected in
series with S, the null point occurs at 50 cm. Determine the values of R and S.
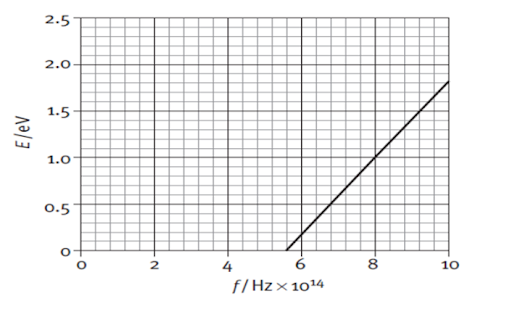
18. The graph below shows the maximum kinetic energy of the
emitted photoelectrons as the frequency of the incident radiation on a sodium
plate is varied.
(a) From the graph determine the maximum frequency of incident radiation that can cause a photoelectric effect.
(b) Calculate the work function for sodium.
(c) Use the graph to calculate the value of the Planck
constant in Js.
19. (a) Figure below shows the experimental setup of Millikan’s oil drop experiment. Find the expression for a charge of an oil drop of radius r moving with constant velocity v in a downward direction using a free body diagram.
(b)What will be the expression for the charge of an oil drop
if the electric force is greater than its weight?
(c) Determine the electric field supplied when the electric
force applied between the two horizontal plates just balances an oil drop with
4 electrons attached to it and mass of oil drop is 1.3x10-14 kg.
OR
(a) A diode can be used as a rectifier. What characteristic
of a diode is used in rectification?
(b) Draw a circuit diagram of full wave rectifier.
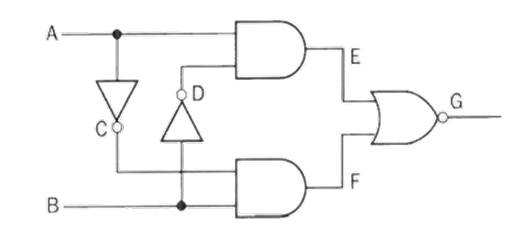
(c) A NOR gate ‘opens’ and gives an output only if both inputs are ‘low’, but an OR gate ‘closes’. An AND gate ‘opens’ only if both inputs are ‘high’, but a NAND gate ‘closes’. Construct a truth table for the circuit shown below including the states at E, F and G.
Group C
20. (a) What is the significance of the negative energy of
the electron in an orbit?
(b) The energy levels of an atom are shown in Fig. below. Which one of these transitions will result in the emission of a photon of wavelength 275 nm? Explain with calculation. (h= 6.64 x10-34Js, C= 3.0x108 ms-1)
(c) Find the expression for the wavelength of radiation
emitted from a hydrogen atom when an electron jumps from higher energy level n2
to the lower energy level n1.
(d) Calculate the magnitude of the wavelength of the second
Balmer series? (R =1.09x107m -1)
21. (a) A student is trying to make an accurate measurement
of the wavelength of green light from a mercury lamp (λ = 546 nm). Using a
double slit of separation of 0.50 mm, he finds he can see ten clear fringes on
a screen at a distance of 0.80 m from the slits. He then tries an alternative
experiment using a diffraction grating that has 3000 lines/cm.
(i) What will be the width of the ten fringes that he can
measure in the first experiment?
(ii) What will be the angle of the second-order maximum in
the second experiment?
(iii) Suggest which experiment you think will give the more
accurate measurement of wavelength (l).
(b) A physics student went to buy polaroid sunglasses. The
shopkeeper gave him two similar-looking sunglasses. In what way he can
differentiate between polaroid sunglasses and non-polaroid sunglasses?
(c) At what angle of incidence will the light reflected from
water (m =
1.3) be completely polarized?
OR
a) In what way does the intensity of sound heard by an
observer change if the distance with the source changes by four times?
b) A train is traveling at 30m/s in still air. The frequency
of the note emitted by the train whistle is 262Hz. What frequency is heard by a
passenger on the other train moving in the opposite direction to the first at
18m/s (i) when approaches the first and (ii) when receding from the first? (
velocity of sound= 340 m/s)
c)
22. (a) What is choke coil?
(b) Why is it preferred over a resistor in ac circuit?
(c) In figures (a), (b) and (c), three ac circuits with equal currents have been shown.
(i) If the frequency of e.m.f.be increased, then what will
be effect on the currents flowing in them? Explain.
(ii) What difference do you expect in the opposition
provided by circuits for the current flow in figure (a) and (b) if given a.c.
e.m.f. is replaced by its equivalent d.c. e.m.f. ?
OR
(a) Define 1 Ampere of current in terms of force between two
parallel current-carrying conductors.
(b) How do you explain the contraction of the solenoidal
coil while the current is passed through it?
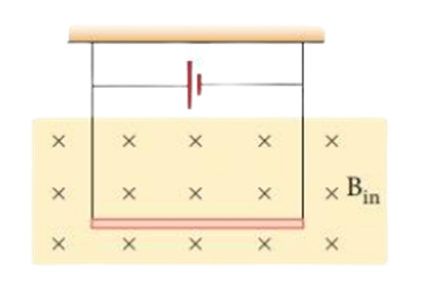
(c) A conductor of linear mass density 0.2 g m-1
suspended by two flexible wires as shown in the figure. Suppose the tension in
the supporting wires is zero when it is kept inside the magnetic field of 1T
whose direction is into the page.
(i) Compute the current inside the conductor.
(ii) If the current determined in part (i) is passed through a 100-turn coil of 100 cm2 area with its axis held perpendicular to the magnetic field of flux density 10 T and plane of coil parallel to the field, how much torque is produced?