XII Physics Model Set
Group A
1. Which of the
following is a correct formula for calculating the radius of gyration of a
rotating object?
A) k2= I/m
B) k= I/m
C) k= m/I
D) k = (I/m)2
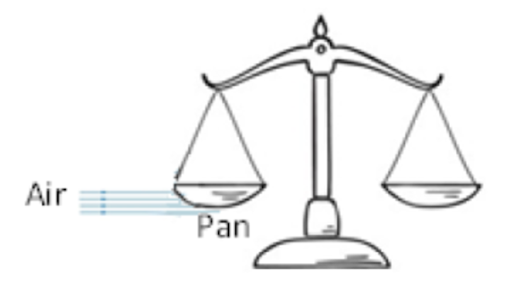
2. A horizontal stream of air is blown under one of the pans of a beam balance
as shown in the figure. What will be the effect of this on the pan?
A) Goes up
B) goes down
C) remains unaffected
D) rotates
3. What will be the
height of a capillary on the surface of the Moon if it is „h‟ on Earth?
A) h
B) h/6
C) 6h
D) zero
4. What is the
coefficient of performance of an ideal refrigerator working between ice point
and room temperature (27°C)?
A) 0
B) 0.1
C) 1
D) 10
5. A thermodynamic system is taken from A to B via C and then returned to A via D as shown in the p-V diagram. The area of which segment of the graph represents the total work done by the system?
A) P1ACBP2P1
B) ACBB’A’A
C) ACBDA
D) ADBB’A’A
6. Which one of the
following directly affects the quality of sound?
A) Shape of the source
B) frequency
C) intensity
D) wave form
7.
A diffraction pattern is obtained using a beam of red light. What
will be the effect on the diffraction pattern if the red light is replaced
with white light?
A) All bright fringes become white.
B) All bright fringes, except the central one, become white.
C) All bright fringes become colourful.
D) All bright fringes, except the central one, become colourful.
8. In which one of the following diagrams the currents are related by the equation I1 – I2 = I3 – I4?
9. A coil having N
turns and cross-section area A carries current I. Which physical quantity does
the product NIA represent?
A) Magnetic flux of the coil
B) magnetic flux density of the coil
C) magnetic moment of the coil
D) magnetic susceptibility of the coil
10. What happens to
the neutral temperature if the cold junction of a thermocouple is decreased?
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Remains the same
D) Approaches inversion temperature
11. What is the point
where the seismic waves start called?
A) Epicentre
B) Hypocentre
C) Metacentre
D) Seismic centre
GROUP B
Short Answer Questions (8 x 5 = 40)
1. (i) Define “surface tension”. [1]
(ii) Establish a relation between surface tension and surface energy of a
liquid. [2]
(iii) Two spherical rain drops of equal size are falling vertically through air
with a certain terminal velocity. If these two drops were to coalesce to form a
single drop and fall with a new terminal velocity, explain how the terminal
velocity of the new drop compares to the original terminal velocity. [2]
2. Angular speed of a rotating body is inversely
proportional to its moment of inertia.
(i) Define „moment of inertia‟. [1]
(ii) Explain why angular velocity of the Earth increases when it comes closer
to the Sun in its orbit. [2]
(iii) If the Earth were to shrink suddenly, what would happened to the length
of the day? Give reason. [2]
OR
(i) State Bernoulli principle. [1]
(ii) Derive Bernoulli‟s equation. [2]
(iii) You can squirt water from a garden hose a considerably greater distance
by partially covering the opening with your thumb. Explain how this works. [2]
3. (i) Define „harmonics‟ in music. [1]
(ii) Calculate the frequency of a monotonous sound produced by a 30 cm long
flute open at both ends and being played in the first harmonic. [Velocity of
sound in air= 330 ms-1] [2]
(iii) The flute mentioned in question (ii) was being played by a passenger on a
stationary bus. The bus then moves uniformly. Explain what change in the pitch
of the flute sound, if any, a person sitting on a bench at the bus park will
feel when the bus starts moving. [2]
4. (i) State the second law of thermodynamics.
[1]
(ii) A refrigerator transfers heat from a cold body to hot body. Does this not
violate the second law of thermodynamics? Give reason. [2]
(iii) In the given figure, a heat engine absorbs Q1 amount of
heat from a source at temperature T1 and rejects Q2 amount
of heat to a sink at temperature T2 doing some external work W.
(a) Obtain an expression for the efficiency of this heat
engine. [1]
(b) Under what condition does the efficiency of such engine become zero
percentage, if at all? [1]
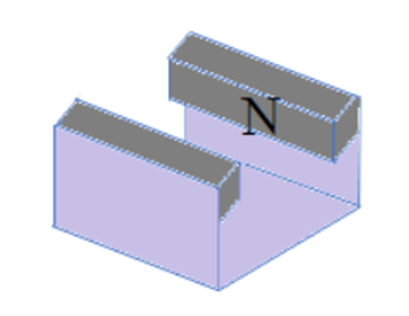
5. A student wants to measure the magnetic flux density
between the poles of two weak bar magnets mounted on a steel yoke as shown in
the figure. The magnitude of the flux density is between 0.02T and 0.04T.
(i) Define Magnetic flux density. [1]
(ii) One way of measuring the magnetic flux density could be the use of a Hall
probe. Suggest one reason why Hall probe is not a suitable instrument to
measure the magnetic flux density for the arrangement shown in the below
figure. [1]
(iii) Another method of measuring the magnetic flux density for the arrangement
shown in the above figure is to insert a current-carrying wire between the
poles of the magnet. Explain how the magnetic flux density can be determined using
this method. You are allowed to use any additional apparatus. [3]
6. (a) Law of electromagnetic induction can be expressed
mathematically as ε = -N(dϕ/dt).
(b) (i) State what the symbols ε and dϕ/dt represents in the equation. [2]
(ii) Explain the significance of the negative sign. [1]
(ii) Two identical copper balls are dropped from the same height as shown in
the figure. Ball P passes through a region of uniform horizontal magnetic field
of flux density B.
Explain why ball P takes longer than ball Q to reach the ground. [2]
7. Ultraviolet radiation of frequency 1.5 × 1015Hz
is incident on the surface of an aluminium plate whose work function is 6.6×10-19J.
(i) Show that the maximum speed of the electrons emitted from the surface of
the aluminium is 8.6 × 105ms–1. [3]
(ii) State and explain what change, if any, occurs to the maximum speed of the
emitted electrons when the intensity of the ultraviolet radiation is increased.
[2]
8. (i) State Bohr‟s postulates of atomic model. [3]
(ii) The figure shows Lymen series of energy transmission in hydrogen atom.
Calculate the frequency of a photon emitted by an electron jumping from the
second excited state to the ground level. [2]
OR
(i) Sketch the symbol of a p-n junction diode and indicate
the polarity of its ends. [1]
(ii) Copy the outline of a diode bridge rectifier and complete it by adding
diodes in the gaps. [2]
(iii) Explain what will happen if one of the four diodes is
damaged so that it stops conducting totally in any direction. Sketch a graph to
show how the pd across the Load RL would vary with time in this
situation. [2]
Group C
Long Answer Questions. (3 × 8 = 24)
9. Earthquake sets rocks and buildings in motion. When a
rock is subjected to compression, a restoring force develops inside it. This
restoring force is given by an equation F= -Ax where x is displacement and A is
a constant.
(i) Prove that this force will make the rock vibrate with simple harmonic
motion. [2]
(ii) Show that the speed of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion is
given by the expression v = ±ω√(A2-x2) where the
symbols carry standard meanings. [2]
(ii) Calculate the maximum speed of a building shaken by S-waves of 21Hz and
amplitude 0.05m. [2]
(iv) Explain why tall buildings are more susceptible to damage by S-waves which
generally have low frequency. [2]
10. The figure below shows the variation of emf and current
with time in a typical LRC circuit.
(i) Explain whether the phase constant is positive or negative. [2]
(ii) Sketch a phasor diagram for the given case. [2]
(iii) Is the circuit more inductive or capacitive? Explain. [2]
(iv) To increase the rate at which energy is transferred to the resistive load,
should the inductance be increased or decreased? Justify your answer. [2]
OR
A student sets up a circuit as shown in the figure given below to measure the emf of a test cell.
i. Explain why he is unable to find a balance point and
state the change he must make in order to achieve the balance.[2]
ii. State how he would recognize the balance point. [1]
iii. He obtained the balance point for distance 37.5cm using
standard cell of emf 1.50V. And for the test cell, the balance distance AB was
25.0 cm. Calculate the emf of the test cell. [2]
iv. He could have used an ordinary voltmeter to measure the
emf of the test cell directly. The student, however, argues that the above
instrument is more precise than an ordinary voltmeter. Justify his logic. [2]
11. (a) Explain what is meant by quantization of charge. [2]
(b) In a Millikan’s oil drop experiment, an oil drop of weight 1.5 x 10-14N
is held stationary between plates 10mm apart by applying a p.d. of 470V between
the plates.
(i) State the condition necessary for the drop to remain
stationary. Also, sketch the forces acting on the oil drop. [2]
(ii) Calculate the charge on the oil drop. [2]
(iii) Explain what would happen if the above oil drop is suddenly struck by a
stray alpha particle. [2]
OR
(a) Derive an expression N= Noe-λt for
a radioactive process where the symbols carry their standard meanings. [3]
(b) A student measured the activity of a sample of radioactive rock. Her
results are presented in the graph.
(i) Explain why the data are scattered. [1]
(ii) Determine the half-life of this sample. [2]
(iii) How will the shape of this curve will change if she repeats the experiment
with a sample with a larger decay constant. Give reason to your answer. [2]